
NIH Grant Opportunity for Researchers – Due Date 8/26/14
NIH Environmental Contributors to Autism Spectrum Disorders R01 Research Project Grant due August 26 (Letter of Intent due 30 days before application). The purpose of this FOA is to stimulate and foster research to (1) identify environmental contributors to risk and expression of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) and (2) understand how environmental factors impact the […]

Autism Groups React to New CDC-Reported Prevalence of 1 in 68 Children
Autism Groups React to New CDC-Reported Prevalence of 1 in 68 Children AUTISM POLICY REFORM COALITION URGES GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL CAUSES, AND FOCUS ON TREATMENT AND SERVICES WASHINGTON, DC (March 27, 2014)—Today, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued the newest autism prevalence statistics. For children born in 2002, the prevalence of […]
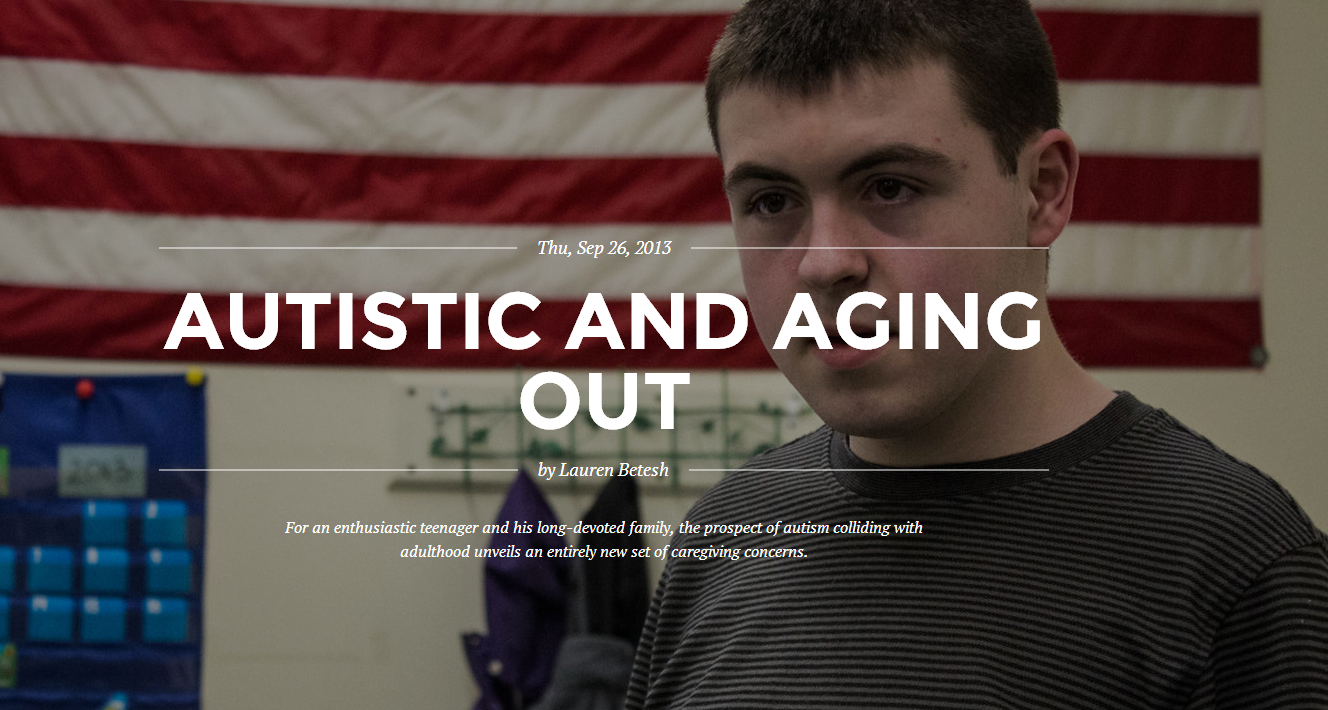
Autistic and Aging Out
Although the subject of the story and video posted here today is not part of the SafeMinds mission, I wish to share them here on my blog page as I believe it will touch many people inside and outside of the autism community. I have more than 16 years of experience with doctors, scientific studies, government agencies, supplements, therapies, school […]

New Study Correlating Mercury and Air Pollution with an Increased Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorders
This new study published by the Harvard School of Public Health demonstrates further evidence of the association between environmental exposure to neurotoxic pollution and increased rates of autism. Not only did the study show mercury air pollution correlated with increased autism rates, it also demonstrated the pollution resulted in increased rates in boys. That this […]

Impact of the DSM-5 Criteria for ASD – Community Update – May 2013
Introduction This month, the American Psychiatric Association will publish the latest edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual – the DSM-5. The manual contains significant changes to the diagnostic criteria for individuals with autism. The name of the category will be changed from Pervasive Developmental Disorder to Autism Spectrum Disorder. The four previous diagnoses: Autistic […]

Selling Sickness and Pharmed Out
As more people become aware of the dark-side of the pharmaceutical industry’s efforts to market their products, an extraordinary series of conferences have been taking place to address to the troubling issue. Most recently, Selling Sickness 2013: People before Profits, brought together more than 225 scholars, healthcare reformers, consumer/patient advocates, journalists, attorneys, and public health officials from around […]


